Don't Miss
Most Read
Trending on GB News
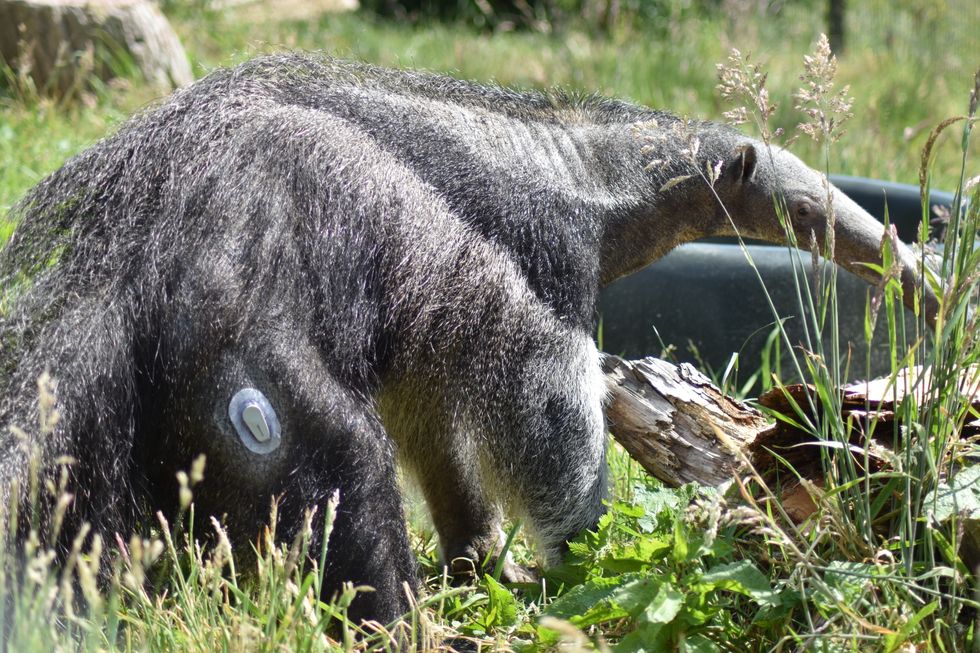
A giant anteater at Edinburgh Zoo is being treated for diabetes, with keepers relying on a device more usually used in humans to monitor her condition.
In the first reported case of its kind, anteater Nala has been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
Keepers have trained her to have daily insulin injections, while a donated glucose monitor is being used to ensure she gets the right dose.
Dr Stephanie Mota, resident veterinary surgeon at the Royal Zoological Society of Scotland, said Nala was diagnosed after exhibiting symptoms similar to those seen in humans with diabetes.
Nala the anteater
RZSS
The donated glucose monitor
RZSS
Dr Mota said: “Keepers first discovered something was wrong when Nala was losing weight despite eating the same amount, or sometimes even more than usual.
“We carried out a full health check under general anaesthetic, running lots of tests, and found that Nala has type 1 diabetes.”
While the condition is known to occur in domestic cats and dogs and in tamandua – a type of anteater – in the wild, no other cases have been reported in giant anteaters.
Dr Mota continued: “Our keepers did an amazing job quickly training Nala to take an insulin injection every day, but the challenge for us was how to continuously monitor her blood glucose levels to ensure she was receiving the perfect dose.
“Taking bloods daily was not an option, and we did initially start monitoring the levels through urine samples but we decided to contact some companies who produced human glucose monitors to try and streamline the process, and find a way which would be the least invasive for Nala.
“Dexcom, leading providers of this technology, kindly donated the monitor to our charity and we were able to apply it during one of her training sessions, which now allows us to check her blood glucose levels through an app remotely.
“Due to her lovely personality, Nala is the ideal candidate for this technology which helps us, and her amazing team of keepers, manage her condition in the best possible way.”